Introduction
An Exercise Stress Treadmill Test also known as ETT is performed to assess how your heart works during stressful physical activity. During exercise the heart rate increases and which makes your heart pump harder and faster in order to supply blood to all parts of your body including your heart. The test reveals any problems within your heart of there are is a compromise in blood supply to heart during exercise.
Other Types of Exercise Stress Test
- Bicycle Exercise Stress Test: Riding a Stationary Bike
- Stress Echocardiogram: Requires medication to increase heart speed
Who is Exercise Stress test for?
- To diagnose coronary artery disease
- To rule out angina as a cause of chest pains
- To diagnosis heat rhythm problems (arrhythmias) at exercise.
- The doctor may use the Test, to guide treatment decisions in adjusting medications, assess timing of valve disease and to assess for heart transplantation and advanced therapies in heart failure.
Before Test
- You may be asked not to eat, drink 2-4 hours before test
- You may need to avoid caffeine the day before and the day of the test.
- You may be asked to stop medications 24- 48 hours before the test, including Beta-blocker/ Calcium channel blockers, which may interfere in the speed of heart (confirm with your doctor)
- Let your doctor know if you are using any other medications and over-the-counter medications before the test, because they might interfere with certain stress tests.
- If you use an inhaler for asthma or other breathing problems, bring it to the test and let your doctor know.
During Test
An ETT is a non-invasive test. This test is simple and can be performed at your doctor's office, a clinic or a hospital room. It involves Treadmill machine, which is similar to what is available in any gym for exercise. You will be asked to expose chest and then the technician will attach sticky patches (electrodes) to your body to help detect and conduct the electrical currents of your heart during exercise. A blood pressure cuff will be attached to your arm to checks your blood pressure during the test. A doctor is present in the room throughout the test and pre-checks will ask you to start test.
The test starts with a slow speed and gradually increases in speed. During test your heart rate will reach to a set target or until you develop symptoms that don't allow you to continue. These signs and symptoms may include:
- Moderate to severe chest pain
- Severe shortness of breath
- Abnormally high or low blood pressure
- An abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmias)
- Dizziness
- Fatigue or tiredness
- Changes in your ECG/EKG
During test your doctor will discuss your safe limits for exercise and decide regarding further continuation of exercise.
Possible risks with test
A stress exercise test is generally safe but some of possible complications are:
- Drop in blood pressure: This may occur during or immediately after exercise, possibly causing you to feel dizzy or faint. This usually recovers quickly. This may be a normal response or related to underlying heart problem (ask your doctor)
- Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias): You may develop some extra beats or fast heart rates (Arrhythmias) during exercise test. You may feel dizzy or fait. This usually recovers quickly. This may be a normal response or related to underlying heart problem (ask your doctor)
- Heart attack (myocardial infarction):Although very rare, but some patient may develop heart attack due to the underlying problem with the heart arteries.
After a Stress Test
After you are asked to stop exercise, you may be asked to stand still for several seconds or sit down on chair for a short period for you to recover. Your ECG/EKG and blood pressure will be monitored for any abnormalities.
When your exercise stress test is complete, you may return to your normal activities unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Results
- The doctor may release the results to you immediately after the test or send the results to the referring physician.
- The doctor may start on any medications or admit you to hospital if there are any significant abnormalities noted.
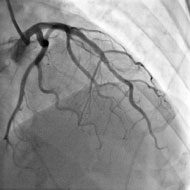
- The doctor may request for further additional tests, such as a coronary angiogram.
How long does the procedure last?
This procedure may take upto 30-40 minutes but may require more timings if any abnormalities noted