Aims of the Guidance
- This protocol is intended to standardize the anticoagulation management for critically-ill patients with COVID19 pneumonia requiring admission to intensive care unit.
Indications:
- Adult patients admitted to Intensive Care Unit with COVID19 Pneumonia OR as per your local guidance for high risk patients.
Contraindication:
- Patients with active bleeding.
- Platelets less than 50,000 per microliter.
- Fibrinogen level less than 1.5 gram per liter.
Protocol
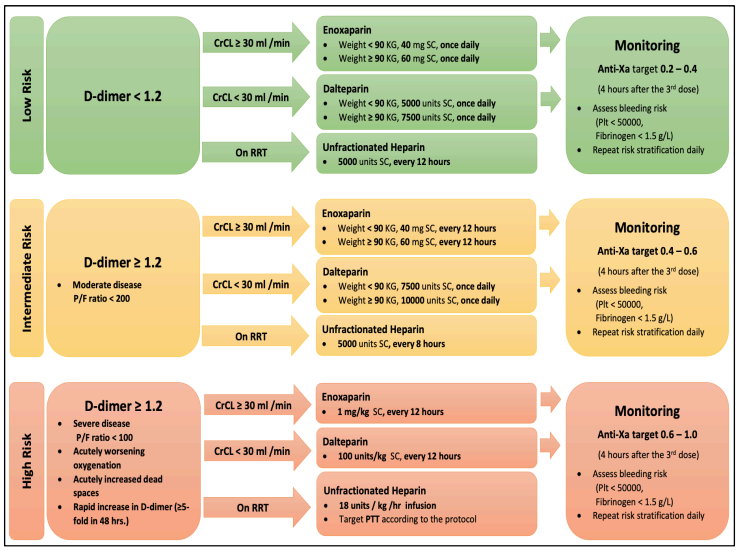
- LOW-RISK GROUP: D-Dimer less than 1.2 mg/L
- If CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min
- Enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight < 90 kg.
- Enoxaparin 60 mg subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight ≥ 90 kg.
- If CrCl < 30 ml/min
- Dalteparin 5,000 units subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight < 90 kg.
- Dalteparin 7,500 units subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight ≥ 90 kg.
- For patients on Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT),
- Unfractionated Heparin 5000 units subcutaneous every 12 hours.
- INTERMEDIATE-RISK GROUP: D-Dimer ≥ 1.2 mg/L and P/F ratio < 200
- If CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min
- Enoxaparin 40 mg subcutaneous every 12 hours for patients with weight < 90 kg.
- Enoxaparin 60 mg subcutaneous every 12 hours for patients with weight ≥ 90 kg.
- If CrCl < 30 ml/min,
- Dalteparin 7,500 units subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight < 90 kg.
- Dalteparin 10,000 units subcutaneous once daily for patients with weight ≥ 90 kg.
- For patients on Renal Replacement Therapy,
- Unfractionated Heparin 5000 units subcutaneous every 8 hours.
- HIGH-RISK GROUP: D-Dimer ≥ 1.2 mg/L, P/F ratio < 100, acutely worsening oxygenation or increasing dead space or rapid increase in D-Dimer ( ≥ 5 folds in 48 hours).
- If CrCl ≥ 30 ml/min,
- Administer Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg subcutaneous every 12 hours.
- If CrCl < 30 ml/min,
- Administer Dalteparin 100 units/kg subcutaneous every 12 hours.
- For patients on Renal Replacement Therapy,
- Administer Unfractionated Heparin intravenous infusion at 18 units/kg/hour targeting aPTT as per protocol.
MONITORING PATIENTS RECEIVING ANTICOAGULATION
- For low-risk patients:
- Receiving LMWH (Enoxaparin or Dalteparin), target Anti-Factor Xa level of 0.2-0.4 units/ml. Blood sample to be collected for analysis 4 hours after the 3rd dose.
- For intermediate-risk patients
- Receiving LMWH (Enoxaparin or Dalteparin), target Anti-Factor Xa level of 0.4-0.6 units/ml. Blood sample to be collected for analysis 4 hours after the 3rd dose.
- For high-risk patients
- Rreceiving LMWH (Enoxaparin or Dalteparin), target Anti- Factor Xa level of 0.6-1.0 units/ml. Blood sample to be collected for analysis 4 hours after the 3rd dose.
- For all patients assess bleeding risk daily (platelet count < 50,000 per microliter, fibrinogen level < 1.5 gm/L).
Algorithm
References
- Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, Gong J, Li D, Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy [Internet]. Wiley Online Library. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd;2020 [cited 2020Apr11].
Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jth.14817 - Makatsariya A.D., Grigoreva K.N., Mingalimov M.A., Bitsadze V.O., KhizroevaJ.K., Tretyakova M.V., Elalamy I., Shkoda A.S., Nemirovskiy V.B., Blinov D.V.,Mitryuk D.V. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome. Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproduction. 0;. (In Russ.)
https://doi.org/10.17749/2313-7347.132 - Poggiali, E., Bastoni, D., Ioannilli, E., Vercelli, A., & Magnacavallo, A. (2020). Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Two Complications of COVID-19 Pneumonia. European Journal of Case Reports in Internal Medicine,
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.12890/2020_001646 - Casey K, Iteen A, Nicolini R, Auten J. COVID-19 pneumonia with hemoptysis: Acute segmental pulmonary emboli associated with novel coronavirus infection [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 8]. Am J Emerg Med.2020; doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.011
- Thachil J. The versatile heparin in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020 Apr 2. doi:10.1111/jth.14821.
- Ling Lin, Lianfeng Lu, Wei Cao & Taisheng Li (2020) Hypothesis for potential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection–a review of immune changes in patients with viral pneumonia, Emerging Microbes & Infections, 9:1, 727-732. DOI: 0.1080/22221751.2020.1746199
- Thachil J, Tang N, Gando S, Falanga A, Cattaneo M, Levi M, et al. ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19 [Internet]. Wiley Online Library. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2020 [cited 2020Apr11].
Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jth.14810. - Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, Fan G, Liu Y, Liu Z, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet 2020.
- Tang, N, Li, D, Wang, X, Sun, Z. Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2020; 18: 844– 847.
- ZhouF,YuT,DuR,FanG,LiuY,LiuZ,XiangJ, Wang Y, Song B, Gu X, Guan L. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020;395:1054–1062.
- Klok FA, Kruip MJ, van der Meer NJ, Arbous MS, Gommers DA, Kant KM, Kaptein FH, van Paassen J, Stals MA, Huisman MV, Endeman H. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res 2020;doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013.
- YaoXH,LiTY,HeZC,PingYF,LiuHW,YuSC, Mou HM, Wang LH, Zhang HR, Fu WJ, Luo T. [A pathological report of three COVID-19 cases by minimally invasive autopsies]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020;49:E009.
- Giannis D, Ziogas IA, Gianni P. Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past. J Clin Virol 2020;9:104362.
- Tang N, Bai H, Chen X, Gong J, Li D, Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost 2020;doi: 10.1111/jth.14817.
- Kreuziger L, Lee A, Garcia D, Cuker A, Cushman M, Connors J. COVID-19 and VTE-anticoagulation.
https://www.hematology.org/covid-19/covid-19-and vteanticoagulation. - Mummery RS, Rider CC. Characterization of the heparin-binding properties of IL-6. J Immunol 2000; 165:5671–569. National Health Service (NHS), Imperial College Health Care anticoagulation protocol for COVID19 patients.
- Boston University Medical Center.